History & Overview
(166 - 129 BCE)
The death of Alexander
the Great of Greece in
323 BCE led to the breakup of the Greek empire as three of his generals fought for supremacy and divided the
Middle East among themselves. Ptolemy secured control of Egypt and the Land of Israel. Seleucus grabbed Syria and Asia Minor, and Antigonus took Greece.
The Land of Israel was thus sandwiched between two of the rivals and,
for the next 125 years, Seleucids and Ptolemies battled for this prize.
The former finally won in 198 B.C. when Antiochus III defeated the Egyptians
and incorporated Judea into his empire. Initially, he continued to allow
the Jews autonomy, but after a stinging defeat at the hands of the Romans he began a program of Hellenization that threatened to force the Jews
to abandon their monotheism for the Greeks' paganism. Antiochus backed
down in the face of Jewish opposition to his effort to introduce idols
in their temples, but his son, Antiochus IV, who inherited the throne
in 176 B.C. resumed his father's original policy without excepting the
Jews. A brief Jewish rebellion only hardened his views and led him to
outlaw central tenets of Judaism such as the Sabbath and circumcision, and defile
the holy Temple by erecting
an altar to the god Zeus, allowing the sacrifice of pigs, and opening
the shrine to non-Jews.
The Jewish Hammer
Though many Jews had been seduced by the virtues of Hellenism,
the extreme measures adopted by Antiochus helped unite the people. When
a Greek official tried to force a priest named Mattathias to make a
sacrifice to a pagan god, the Jew murdered the man. Predictably, Antiochus
began reprisals, but in 167 BCE the Jews rose up behind Mattathias and
his five sons and fought for their liberation.
The family of Mattathias became known as the Maccabees, from the Hebrew word for "hammer,"
because they were said to strike hammer blows against their enemies.
Jews refer to the Maccabees, but the family is more commonly known as
the Hasmoneans.
Like other rulers before him, Antiochus underestimated
the will and strength of his Jewish adversaries and sent a small force
to put down the rebellion. When that was annihilated, he led a more
powerful army into battle only to be defeated. In 164 BCE, Jerusalem was recaptured by the Maccabees
and the Temple purified, an
event that gave birth to the holiday of Chanukah.
Jews Regain Their Independence
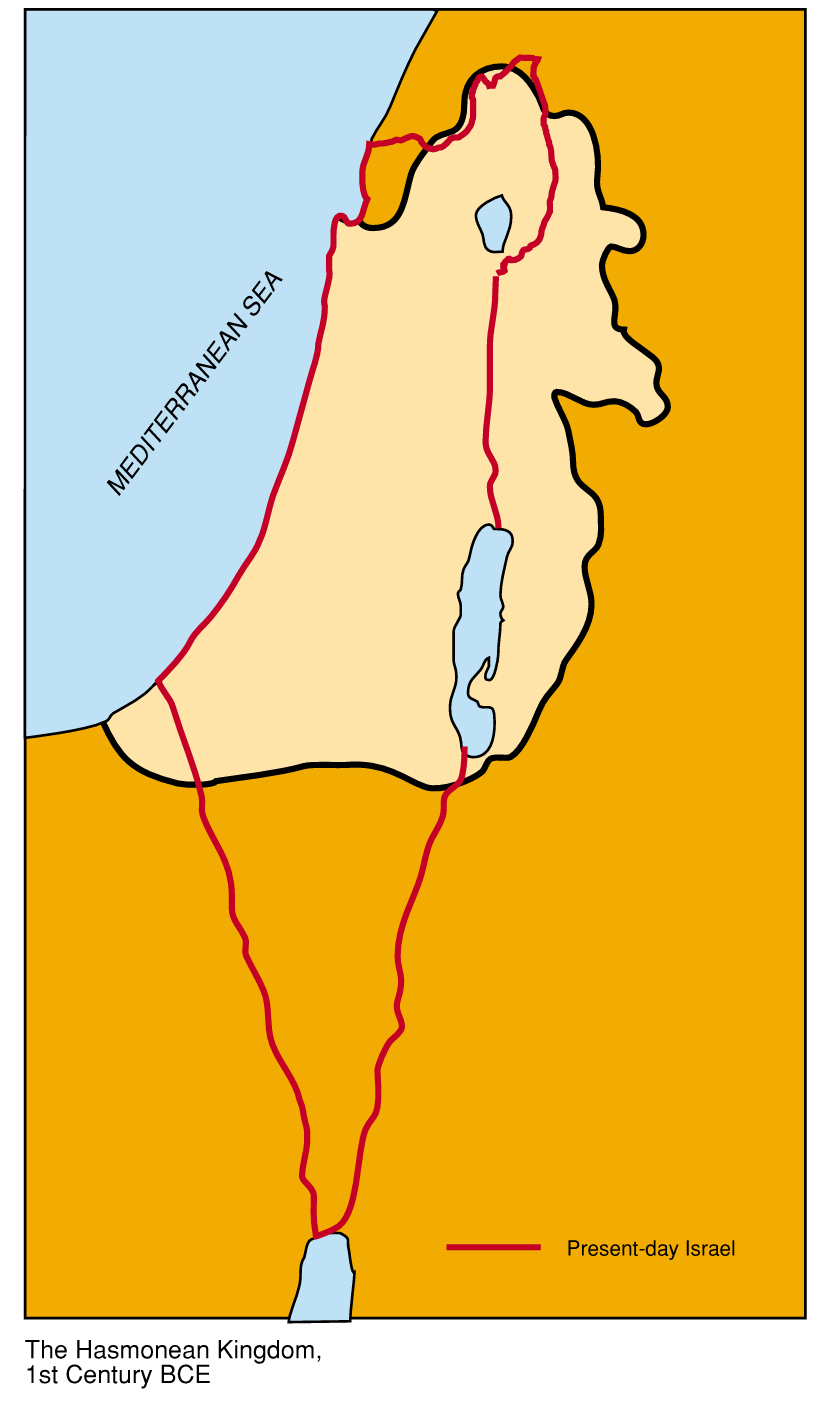 It
took more than two decades of fighting before the Maccabees forced the
Seleucids to retreat from the Land of Israel. By this time Antiochus had died
and his successor agreed to the Jews' demand for independence. In the
year 142 BCE, after more than 500 years of subjugation, the Jews were
again masters of their own fate. It
took more than two decades of fighting before the Maccabees forced the
Seleucids to retreat from the Land of Israel. By this time Antiochus had died
and his successor agreed to the Jews' demand for independence. In the
year 142 BCE, after more than 500 years of subjugation, the Jews were
again masters of their own fate.
When Mattathias died, the revolt was led by his son
Judas, or Judah Maccabee,
as he is often called. By the end of the war, Simon was the only one
of the five sons of Mattathias to survive and he ushered in an 80-year
period of Jewish independence in Judea,
as the Land of Israel was now called.
The kingdom regained boundaries not far short of Solomon's realm and Jewish life flourished.
The Hasmoneans claimed not only the throne of Judah,
but also the post of High Priest. This assertion of religious authority
conflicted with the tradition of the priests coming from the descendants
of Moses' brother Aaron and the tribe of Levi.
It did not take long for rival factions to develop
and threaten the unity of the kingdom. Ultimately, internal divisions
and the appearance of yet another imperial power were to put an end
to Jewish independence in the Land of Israel for nearly two centuries.
Sources: Mitchell G. Bard,The
Complete Idiot's Guide to Middle East Conflict. 4th
Edition. NY: Alpha Books, 2008.
|